Product
Blood Glucose Management: Modern Strategies for Better Metabolic Health
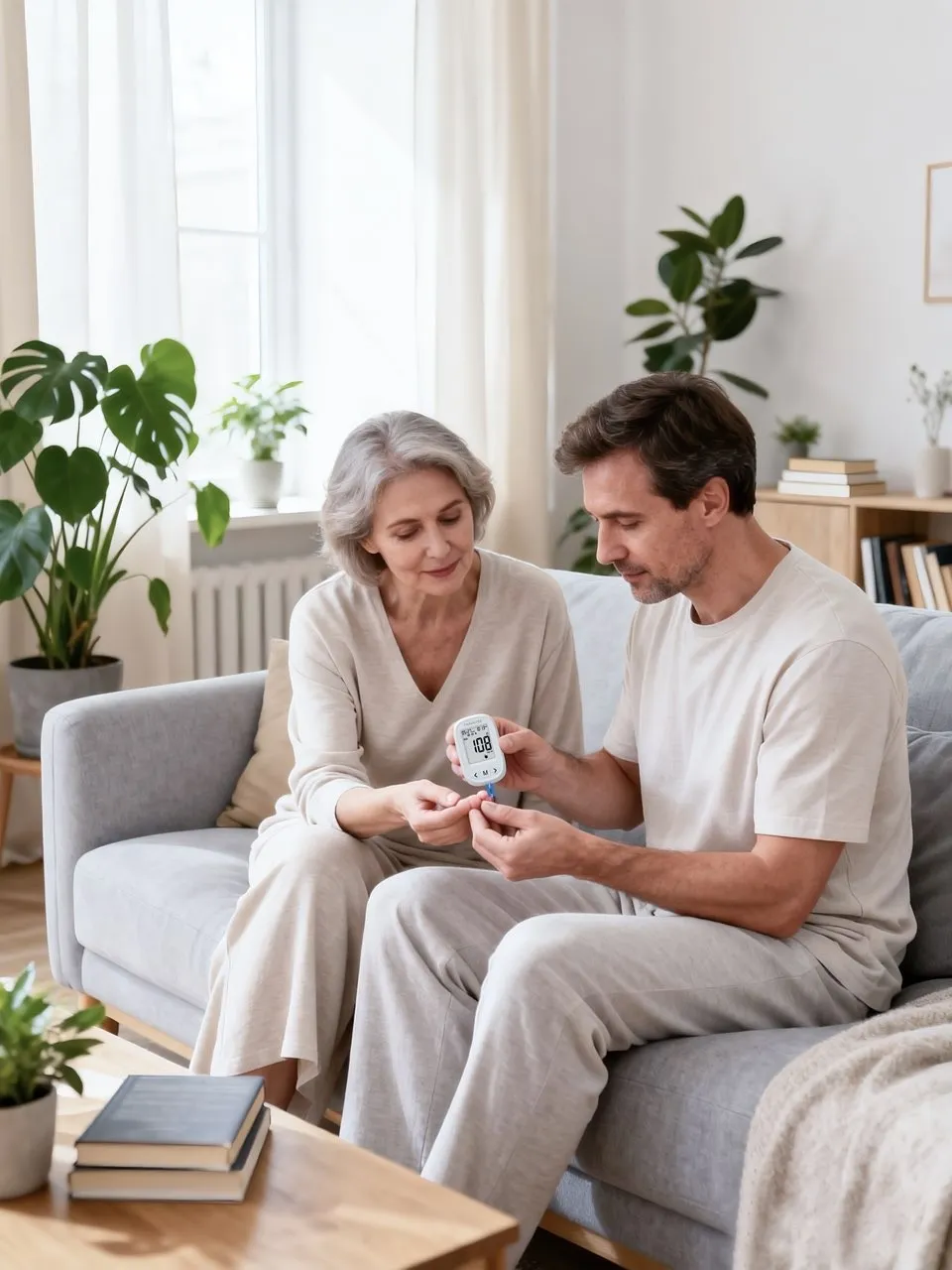

Keeping blood glucose within a healthy range is essential for preventing diabetes complications, improving energy levels, and supporting long-term metabolic wellness. Whether you live with diabetes, prediabetes, or simply want better health insights, understanding glucose control is key.
Why Blood Glucose Management Matters
Blood glucose is the body’s primary fuel. However, consistently high levels damage blood vessels, nerves, and vital organs. The standard indicator for long-term glucose control is HbA1c, which reflects average blood sugar over several weeks. Many health organizations recommend a target below 7% for most adults with type 2 diabetes.
Daily Monitoring: A Cornerstone of Glucose Control
Monitoring reveals how meals, stress, exercise, and sleep affect blood sugar.
1. Finger-Prick Glucose Tests
Still widely used and reliable for spot-checking glucose.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
CGMs reveal real-time trends and reduce glucose variability—especially valuable for diabetes self-management.
3. Emerging Non-Invasive Methods
Recent research explores sensor-based systems that estimate glucose from sweat or optical signals, paving the way for painless monitoring in the future.
Lifestyle Factors That Improve Glucose Levels
1. Smart Eating Habits
· Reduce refined carbohydrates
· Increase fiber-rich foods
· Balance meals to prevent rapid sugar spikes
2. Physical Activity
Exercise improves insulin sensitivity. Even short post-meal walks can noticeably reduce glucose spikes.
Digital exercise programs and mobile apps have shown early promise in helping individuals improve glucose stability through personalized feedback.
The Link Between Weight and Glucose Control
Excess body fat, especially abdominal fat, reduces insulin sensitivity. Research shows that modest weight loss significantly improves fasting glucose and HbA1c levels. Regular weight tracking helps reinforce healthy habits and supports better metabolic outcomes.
Conclusion
Effective blood glucose management combines smart monitoring tools, informed eating habits, consistent exercise, and healthy weight control. Staying updated with modern research and technology empowers individuals to take proactive control of their metabolic health.
Keeping blood glucose within a healthy range is essential for preventing diabetes complications, improving energy levels, and supporting long-term metabolic wellness. Whether you live with diabetes, prediabetes, or simply want better health insights, understanding glucose control is key.
Why Blood Glucose Management Matters
Blood glucose is the body’s primary fuel. However, consistently high levels damage blood vessels, nerves, and vital organs. The standard indicator for long-term glucose control is HbA1c, which reflects average blood sugar over several weeks. Many health organizations recommend a target below 7% for most adults with type 2 diabetes.
Daily Monitoring: A Cornerstone of Glucose Control
Monitoring reveals how meals, stress, exercise, and sleep affect blood sugar.
1. Finger-Prick Glucose Tests
Still widely used and reliable for spot-checking glucose.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
CGMs reveal real-time trends and reduce glucose variability—especially valuable for diabetes self-management.
3. Emerging Non-Invasive Methods
Recent research explores sensor-based systems that estimate glucose from sweat or optical signals, paving the way for painless monitoring in the future.
Lifestyle Factors That Improve Glucose Levels
1. Smart Eating Habits
· Reduce refined carbohydrates
· Increase fiber-rich foods
· Balance meals to prevent rapid sugar spikes
2. Physical Activity
Exercise improves insulin sensitivity. Even short post-meal walks can noticeably reduce glucose spikes.
Digital exercise programs and mobile apps have shown early promise in helping individuals improve glucose stability through personalized feedback.
The Link Between Weight and Glucose Control
Excess body fat, especially abdominal fat, reduces insulin sensitivity. Research shows that modest weight loss significantly improves fasting glucose and HbA1c levels. Regular weight tracking helps reinforce healthy habits and supports better metabolic outcomes.
Conclusion
Effective blood glucose management combines smart monitoring tools, informed eating habits, consistent exercise, and healthy weight control. Staying updated with modern research and technology empowers individuals to take proactive control of their metabolic health.

